-40%
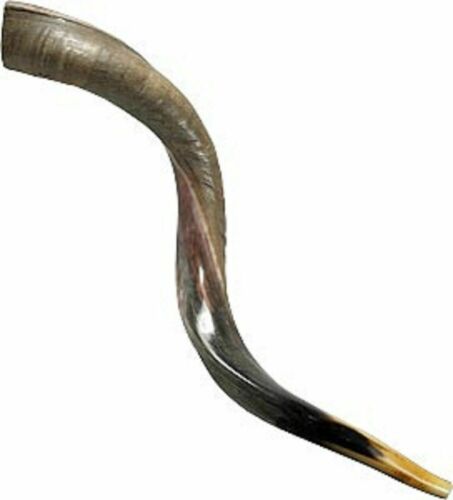
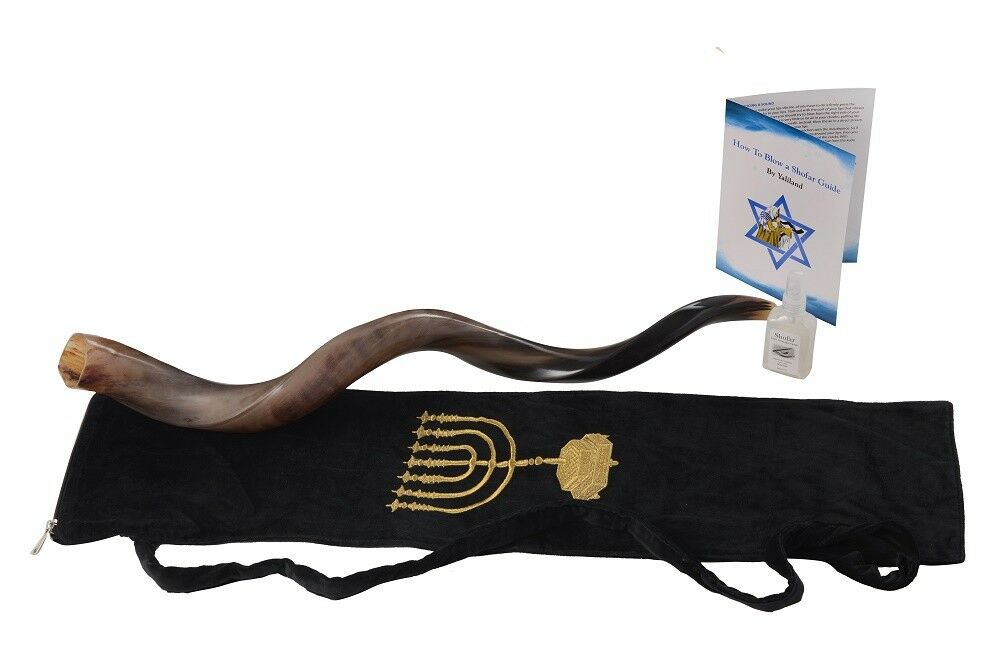
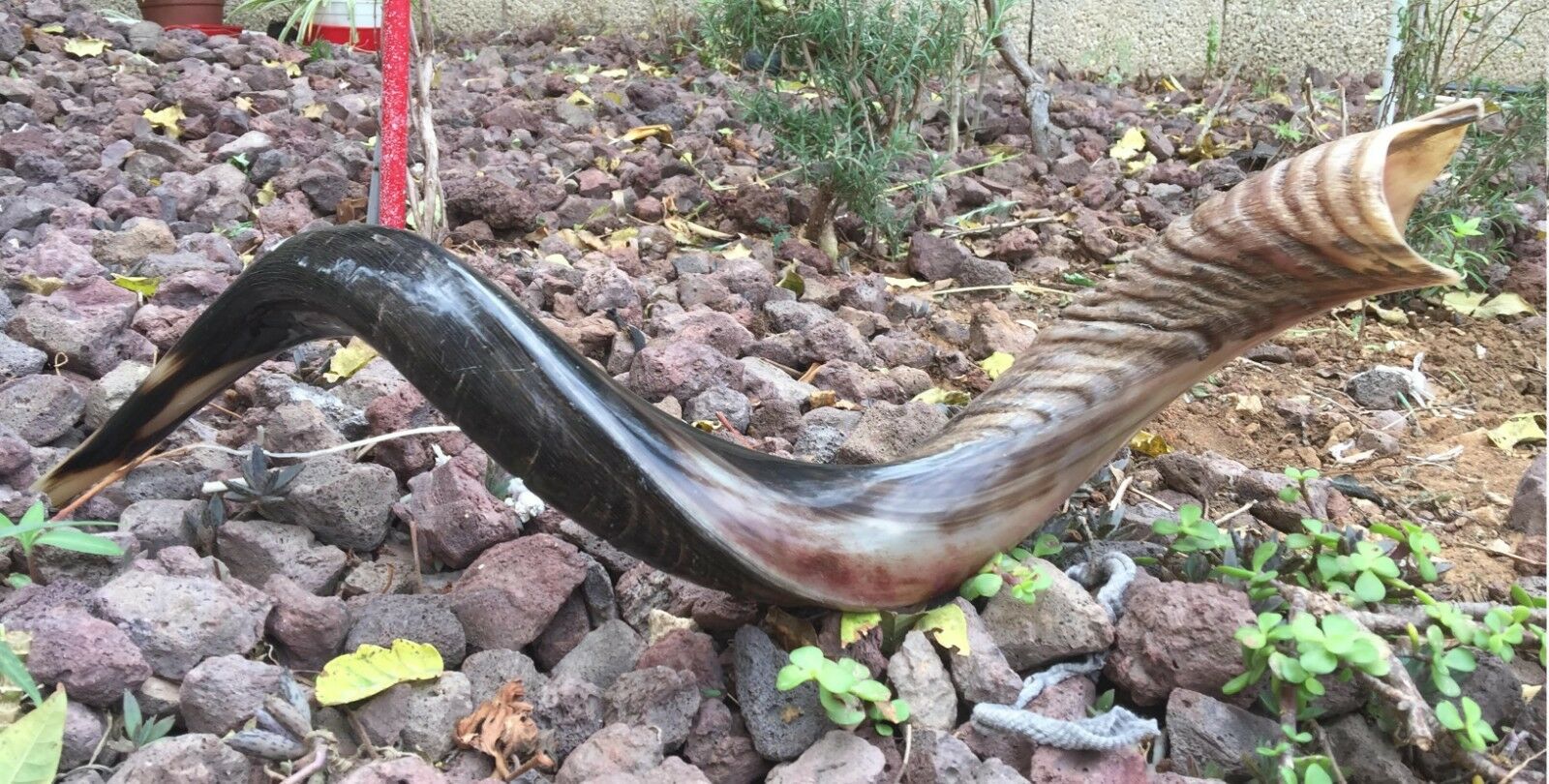
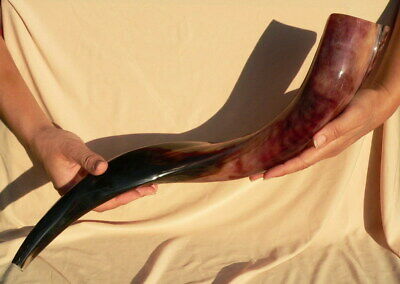
22" Large Full Polish SHOFAR Kosher Jewish Kudu Trumpet Sound Blow in Zion Horn
$ 33.85
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
AuthenticShofar, Trumpet Blow Horn
High Quality,
Fully Polished
Made from Kudu (Antelope) Horn
Brand New, Genuine Kosher, Handcrafted in Israel
medium tone sound, loud and clear
Strong and durable, curved Shofar, hand made in Israel
from high quality
African Antelope Kudu's horns. The horns are drilled, shaped and partly polished, showing natural texture and original colors. All Shofars are cleaned and sterilized.
Certified Kosher by the Israeli Chief Rabbinate.
Each Shofar is handpicked and tested to ensure high quality.
Approximate Size (Length*) :
22-23 inch / 55-60 cm
(Sizes will slightly vary from Shofar to Shofar)
* Length is measured on the circumference -
from tip to tip - from the mouthpiece to the shofar's "trumpet" opening
Makes a Good Sound !!
But you must know how to blow, see "free" directions below
Shipping from Israel, arrival time 2-3 weeks
The Shofars come in
assorted different colors,
we cannot guarantee any color
Click here to see more
Jewish Shofars
- Kudu and Ram Horns in store
Click here for more
religious gifts
in store
Authentic Judaica gift from Israel, the Shofar is nice for display and for use, usually we blow the horn around the Jewish new year, when people are soul seeking and praying for answers and forgiveness. It is a great Mitzvah to hear the Shofar blows at synagogues at Rosh Hashanah and Yom Kippur (the high Jewish holidays), and take our prayers high and through the doors of the sky, to be heard and answered, and hopefully fulfilled.
Liorel Art from Israel
Directions for blowing the Shofar
: Hold the Shofar up with the mouthpiece flat (horizontal), usually against the SIDE of your mouth. The lips should be straight and sealed - and only the little part that is covered by the Shofar's mouthpiece should "tremble" apart , when blowing HARD through the shofar. It is a bit like a long continuous spitting from the side of your mouth. Try holding your lips tight with your fingers and let air blow through the side - the trembling lips make the sound, and the horn amplifies it OUT LOUD (Btw the Australian Didgeridoo works on the same idea). Blowing long and clear blows
takes some good practice and patience, but once you get the idea, it is very easy and enjoyable (of course if your neighbors don't mind)
Directions for storage
: store in a cool and dry place. No special maintenance needed - the shofar is a live tissue (bit like nails). Using wax, detergents, solvents etc will harm it.
Traditional ram's horn shofars are made from the horns of sheep while Yemenite shofars are made from the horns of kudu antelope. Kudu are found almost exclusively in eastern and southern Africa. These true horns, unlike the antlers of deer, have a bony core that is actually an extension of one of the bones of the animal's skull. The specialized layer of skin that covers this core of bone contains the protein keratin that makes the horn, and later the shofar, extremely tough and durable.
No two animal horns look alike and no two shofars sound exactly the same. As the ram and kudu grow older, their horns get larger and become more and more twisted into a curve or even a spiral, especially with rams. Horns of older rams often form two or three complete loops. Larger ram's horn shofars are rare and more difficult to get nowadays
More on the shofar: A
shofar
[?o'fa?]
(
Hebrew
:
????
(
help
·
info
)
) is a
horn
, traditionally that of a
ram
, used for
Jewish
religious purposes. Shofar-blowing is incorporated in
syna
gogue
services on
Rosh Hashanah
and
Yom Kippur
. Shofars come in a variety of sizes.
Bible and rabbinic literature
[
edit source
|
edit
beta
]
The
shofar
is mentioned frequently in the
Hebrew Bible
, the
Talmud
and
rabbinic literature
. The blast of a shofar emanating from the thick cloud on
Mount Sinai
made the
Israelites
tremble in awe (Exodus 19:16).
Shofar (by Alphonse Lévy) Caption says: "To a good year"
The shofar was used to announce holidays (Ps. lxxxi. 4), and the
Jubilee year
(Lev. 25:9). The first day of the seventh month (
Tishri
) is termed "a memorial of blowing" (Lev. 23:24), or "a day of blowing" (Num. 29:1), the shofar. They were for signifying the start of a war (Josh. 6:4; Judges 3:27; 7:16, 20; I Sam. 8:3). Later, it was also employed in processions (II Sam. 6:15; I Chron. 15:28), as musical accompaniment (Ps. 98:6; comp. ib. 47:5) and eventually it was inserted into the temple orchestra by David (Ps. 150:3). Note that the 'trumpets' described in Numbers 10 are a different instrument, described by the Hebrew word 'trumpet' (
Hebrew
:
??????
?; hasosrah), not the word for shofar (
Hebrew
:
????
?).
The
Torah
describes the first day of the seventh month (1st of Tishri = Rosh ha-Shanah) as a
zikron teru?ah
(
Hebrew
:
????? ?????
?; memorial of blowing; Lev. xxiii) and as a
yom teru?ah
(
Hebrew
:
??? ?????
?; day of blowing; Num. 29). This was interpreted by the Jewish sages as referring to the sounding of the shofar.
In the
Temple in Jerusalem
, the shofar was sometimes used together with the
trumpet
. On New Year's Day the principal ceremony was conducted with the shofar, which instrument was placed in the center with a trumpet on either side; it was the horn of a
wild goat
and straight in shape, being ornamented with gold at the
mouthpiece
. On fast days the principal ceremony was conducted with the trumpets in the center and with a shofar on either side. On those occasions the shofarot were
rams' horns
curved in shape and ornamented with silver at the mouthpieces. On Yom Kippur of the
jubilee year
the ceremony was performed with the shofar as on New Year's Day.
On Rosh Hashanah and other full holidays (Day of Atonement, Ingathering of the harvest (
Sukkot
), Passover and the Feast of Weeks – Pentecost) a single Priest perfected two sacrifices in honor of the full holiday, (Note that festivals such as Hanukah and Purim, are not considered full holidays requiring an extra sacrifice). On Rosh Hashanah, something special occurred during the special sacrifice. Arguably two Shofar Sounders played the long notes and one Trumpet player played the short note. Accordingly, Rosh HaShanah is called Yom Teruah (the day of the blast) Otherwise, the Trumpets had "top billing." Rosh Hashanah27a, supports this claim: "Said Raba or it may have been R. Joshua B. Levi: What is the scriptural warrant for this? – Because it is written, "With trumpets and the sound of the Shofar shout ye before the King in the Temple, we require trumpets and the sound of the Shofar; elsewhere not."
[1]
Indeed, on Yom Kippur, the Shofar was sounded to announce the
Jubilee Year
(every 50 years, Jews were granted forgiveness, debts were forgiven, indentured Israelites were granted freedom, and the fields "shall become owned by the priests." Shofar first indicated in Yovel (Jubilee Year - Lev. 25:8-13). Indeed, in Rosh Hashanah 33b, the sages ask why the Shofar sounded in Jubilee year. Further support
[
clarification needed
support of what?
]
is found in Rosh Hashanah 29a, where the Talmud talks of trumpets for sacrifices but Shofar in the Jubilee Year does not apply to priests who are exempt from the obligations of the jubilee. Perhaps,
[
citation needed
]
we have the first mention of Shofar Sounding by non-Priests. Perhaps the first distancing away from the Sacrificial Cult.
[
citation needed
]
Otherwise, for all other special days, the Shofar is sounded shorter and two special silver Trumpets announced the sacrifice. When the trumpets sound the signal, all the people who were within the sacrifice prostrate themselves, stretching out flat, face down and on the ground.
The shofar was blown in the times of
Joshua
to help him capture
Jericho
. As they surrounded the walls, the shofar was blown and the Jews were able to capture the city. The shofar was commonly taken out to war so the troops would know when a battle would begin. The person who would blow the shofar would call out to the troops from atop a hill. All of the troops were able to hear the call of the shofar from their position because of its distinct sound.
[
citation needed
]
Post-Biblical times
[
edit source
|
edit
beta
]
In
post-Biblical
times, the shofar was enhanced in its religious use because of the ban on playing musical instruments as a sign of mourning for the destruction of the temple. (It is noted that a full orchestra played in the temple.) The shofar continues to announce the New Year,
[2]
and the new moon,
[
dubious
–
discuss
]
, to introduce
Shabbat
,
[
dubious
–
discuss
]
to carry out the commandment to sound it on Rosh Hashanah, and to mark the end of the day of fasting on Yom Kippur once the services have completed in the evening.
[3]
Secular uses have been discarded (see a notable exception in a section
further down
).
[4]
The shofar is primarily associated with Rosh Hashanah. Indeed, Rosh Hashanah is called "Yom T’ruah" (or "Yom Teruah") (the day of the shofar blast). In the
Mishnah
(book of early rabbinic laws derived from the
Torah
), a discussion centers on the centrality of the shofar in the time before the destruction of the second temple (70 AD). Indeed, the shofar was the center of the ceremony, with two silver trumpets playing a lesser role. On other solemn holidays, fasts, and new moon celebrations, two silver trumpets were featured, with one shofar playing a lesser role. The shofar is also associated with the
jubilee year
in which, every fifty years, Jewish law provided for the release of all slaves, land, and debts. The sound of the shofar on Rosh Hashanah announced the jubilee year, and the sound of the shofar on Yom Kippur proclaimed the actual release of financial encumbrances.
The
halakha
(Jewish law) rules that the shofar may not be sounded on Shabbat due to the potential that the ba’al tekiyah (shofar sounder) may inadvertently carry it which is in a class of forbidden Shabbat work.
[5]
The historical explanation is that in ancient Israel, the shofar was sounded on Shabbat in the temple located in Jerusalem. After the temple’s destruction, the sounding of the shofar on Shabbat was restricted to the place where the great
Sanhedrin
(Jewish legislature and court from 400 BCE to 100 C.E.) was located. However, when the Sanhedrin ceased to exist, the sounding of the shofar on Shabbat was discontinued.
[6]
The shofar says, "Awake, sleepers from your sleep, and slumberers arise from your slumber!" Mishneh Torah, Laws of Repentance 3:4.
[7]
Mitzvah
[
edit source
|
edit
beta
]
The Sages indicated that the
mitzvah
was to hear the sounds of the shofar. They went so far as to consider a shofar blown into a pit or cave and to decide whether a person who hears the original sound or the echo has fulfilled the mitzvah. Mishnah (Rosh Hashanah 27b). The Shulchan Aruch sums up that if the hearer hears the reverberation, the mitzvah is not valid. However, if the listener perceives the direct sounds, he fulfils the mitzvah.
[8]
Thus, most modern halakhic authorities hold that hearing a shofar on the radio or the Internet would not be valid to satisfy the mitzvah because "electronically reproduced sounds do not suffice for mitzvot that require hearing a specific natural sound. . . . However, one should consult a competent rabbi if an unusually pressing situation arises, as some authorities believe that performing mitzvot through electronically reproduced sound is preferable to not performing them at all."
[9]
According to
Jewish law
women and minors are exempt from the commandment of hearing the shofar blown (as is the case with any positive, time-bound commandment), but they are encouraged to attend the ceremony.
If the Baal Tekiyah (shofar sounder) blows with the intention that all who hear will perform the mitzvah, then anyone listening—even someone passing by—who intends to hear the Shofar can perform the mitzvah because the community blower blows for everybody. If the listener stands still, it is presumed he intends to hear.
[10]
If one hears the blast but with no intention of fulfilling the mitzvah, then the mitzvah has not been fulfilled.
Qualifications
[
edit source
|
edit
beta
]
The expert who blows (or "blasts" or "sounds") the shofar is termed the
Tokea
(lit. "Blaster") or
Ba'al T'qiah
(lit. "Master of the Blast"). Being a Ba'al T'qiah (shofar sounder) is an honor. Every male Jew is eligible for this sacred office, providing he is acceptable to the congregation. "The one who blows the shofar on Rosh Hashanah . . . should likewise be learned in the Torah and shall be God-fearing; the best man available." If a potential choice will cause dissension, he should withdraw his candidacy, even if the improper person will be chosen.
[11]
If a blind blower was dismissed, but the community did not find a blower as proficient, he should be appointed as community blower.
The Shulchan Aruch discusses who is fit to blow the shofar on behalf of a congregation:
Anyone not obligated to fulfill the mitzvah of sounding the shofar cannot fulfill the commandment for (cover) another whose duty it is to perform the mitzvah.
Although a woman (who is exempt from this mitzvah because it is time bound) may not blow the shofar for men (whose duty it is to perform the mitzvah), a female
Ba'alat
T'qiah may intone the shofar for herself and other women. Similarly, she may say a blessing over the mitzvah even though it is not mandatory (the requisite blessing contains the words "asher kid'shanu b'mitzvotav v’tzivanu", "who sanctified us with His commandments [mitzvot] and commanded us to ...", but women are not commanded in this mitzvah).
Only a freeman (not even a slave who will become free in the next month) can be a Ba'al T'qiah.
[12]
The
Ba'al T'qiah
shall abstain from anything that may cause ritual contamination for three days prior to Rosh Hashanah.
[13]
from wikipedia
Feel Free to contact us with any question
Liorel, Art from Israel
Find a special gift
Unique art works & gifts, handmade by Israeli artists
Vintage antiques & collectibles from the early days of Israel
Ordering & Shipping Information
100% customer satisfaction guaranteed.
We are a small team dedicated to your service and always want to make sure that you are happy. If you're not satisfied - we're not satisfied.
Worldwide Shipping from Israel.
All orders are insured for loss or damage. Wrapping and packing are done with great care, to ensure safe arrival of the goods.
Combined Shipping:
Order More - Pay Less. We are happy to combine shipping costs as possible, it saves us and you and the environment too!
If you think of purchasing more items from store - please add all items to the shopping cart, the shipping price combines automatically for each additional item.
Shipping price is based on weight and includes the cost of Insurance, handling and packaging, packing materials.
Shipping Options:
Standard, Express and Sea mail. For Express or Sea mail please contact us for a price quote.
Estimated Delivery Time:
By Standard Mail: 10-15 business days (2-3 weeks)
. Express mail: 5-8 business days.
Sea Mail: 1.5-2 months. This is the average delivery time to most places in the world.
Please check the estimated delivery time to your country before purchase (it is written on the item page).
It is best to order ahead of time, as to some countries shipping can take longer than usual. We appreciate your help and patience.
Shipping Enquiries and Delays:
Shipping depends on the final location and the mail services of each country, and delivery times might take
up to 35 business days,
or even more during holidays or to distant locations.
Please contact us if you haven’t received your order within 4 weeks, by marking “I have a question about item”,
and we will solve the problem to your full satisfaction. Remember, once we put the parcel in the post office we depend on the mail services to do their job efficiently and fast.
Returns and other issues
after arrival of goods
:
We always care for your full satisfaction. Please contact us via eBay messages before processing a return, as most situations can be solved faster without going through the process. When contacting us please mark "I have a question about item".
Handling time
can take up to 5 Business days. For some handcrafted items or custom orders it may take more, as stated in the shipping section on item page.
Payment:
All major credit cards are accepted with
Paypal
. Payment must be made within
two weeks
. If you need more time please let us know in advance.
For more information please see our
Ordering & Shipping Page
Thank you for visiting!
Similar
words : Jewish praying synagogue Ashkenazi Sefardi Sefaradi prayer service temple minyan Shaharit Mincha Minkha
Arvith Arvit succot succoth Sukkot Sukot Shavuos shavuot shavuoth pessach Pessah pesach pesah pasach
passover Yom Kippur Kipur atonement days yamim noraim new year rosh hashanah
Hashana Judaica Shabbat Shabat Sabbath Judaism jew
Similar
words : synagogue prayer service temple minyan Shaharit Mincha Minkha
Maariv Arvith Arvit succot succoth shavuot shavuoth pessach pesach pasach
passover Yom Kippur Kipur rosh hashanah Related subjects: Zion, Judaism, religious, religion, holy script, Hebrew, sifrei kodesh,jewish, jew,jews, Judaism, bible, seforin, sefarim, kodesh book, old, antique, , halacha, ,halakha, rabbi, rabbinic,. antiquarian .juif, juive, juden , Judisch, Judische, Bucher, Ebreo, Hebraica, Hebreo, Art, Artist, Artistic, Artists, Illustration, Illustrato, haebraische, judaika , judio, Shabbat Kodesh Sabbath Blessing Sabath times Sabat kabbalat Shabbos Shabos Shabbes Mezuzah case parchment Shema Yisrael Shma Israel kosher Tanakh Tnach Torah bible Gvil Ashkenazi Sephardi Sepharadic Beit Yosef Ari Jewish Judaica Hebräisch Hebrew psalms judisch Judisches Jew Mitzvah Rabbi Blessing Holy Shabes Kabalat Shabbas Shabat candles Chabbat Kiddush Chabat koddesh Schabbat Schabbos Schabes judisch Mitzvah jew Blessing Jewish festival holiday Passover table Spring festival Pesach Pesah Israelites Israeli 12 tribes of Israel Pessach ten commandments Bnei yisrael people of Israel tables of the covenant Tradition Religion Ritual Mitzvah Torah Shalom Israeli Hebrew calendar Shofar Ram horn Praying Prayer Tefila Synagogue Beit Knesset biblical Bible Mishnah Halakha Halacha Torah Tanakh Yiddish Siddur, Holy Temple in Jerusalem, Beit Ha-Mikdash. High Holidays,Sukot Sukkot Yom Kippur Beit Ha-Mikdash, hasidic Ashkenaz, ashkenazic judaism Holy Land Canaan
Yerushalayim, yerushalem, yerushalaim Torah Tora bible bilical